Dragon fruit, a super fruit recently introduced in India, is considered to be a promising, valuable fruit crop. The fruit has a very appealing color and mellow mouth-melting pulp with a black edible seed embedded in the pulp along with an enormous nutritional value that attracts farmers from various parts of India to cultivate this fruit crop originated in Mexico, Central India, and South America. It is a long day plant with a beautiful night-blooming flower, nicknamed "Noble Woman" or "Queen of the Night." The Dragon fruit is called pitaya because of the bracts or scales on the surface of the fruit, and hence the word pitaya means "the scaly fruit'.' Pitaya fruit is one of the most nutritious and rare fruits of the world. It's a favorite for many, especially people of Asian origin.

Proximate nutraceutical values in 100 g edible portion of white-flesh dragon fruit are as follows:
| Principle | Nutritive value per 100 g |
|---|---|
| Moisture | 85.3 % |
| Protein | 1.10 mg |
| Fat | 9.57 mg |
| Crude fibre | 1.34 mg |
| Energy | 67.70 Kcal |
| Carbohydrate | 11.2 mg |
| Glucose | 5.70 mg |
| Fructose | 3.20 mg |
| Sorbitol | 0.33 mg |
| Vitamin C | 3.00 mg |
| Vitamin A | 0.01 mg |
| Niacin | 2.80 mg |
| Calcium | 10.20 |
| Iron | 3.37 |
| Magnesium | 38.90 |
| Phosphorus | 27.75 |
| Potassium | 272.0 mg |
| Sodium | 8.90 mg |
| Zinc | 0.35 mg |
1] Hylocereus undatus: Known as Pitahaya, the variety has a white flesh with pink skin. The fruit is 6-12 cm in length and 4-9 cm in thickness with edible black seeds.
2] Hylocereus Polyrhizus: It is also known as Red Pitaya, it is recognized by its red flesh with its pink skin. It is native to Mexico but is now grown in many countries.
3] Hylocereus Costaricencis: The variety is known for its violet red flesh and pink skin. It is also known as Costa Rican Pitaya as it is native to Costa Rica. The fruit is magenta and the seeds are pear-shaped.
4] Hylocereus (Selenicerus) Megalanthus: This variety is native to South America and is characterized by its white flesh with yellow skin.

There are two ways of growing dragon fruit, the first being the use of seeds and the second of which is the use of plant sampling. Seeds take three years until the plant is large enough to be used so that farmers usually opt for the cutting process. The length of the sapling should be 20 cm and should be cut off from the mother plant and left in the shade for 5-7 days before planting in the field.
While being planted the distance between the dragon fruit plants depends on whether the support used is vertical or horizontal. In the case of vertical support, the distance between the plants maybe 2-3 meters, but in the case of horizontal support, the distance is reduced to almost 50 cm and allows intensive farming.
The vertical support should be between 1 to 120 meters high, while the horizontal support should be between 1.40 to 1.60 meters for appropriate growth.
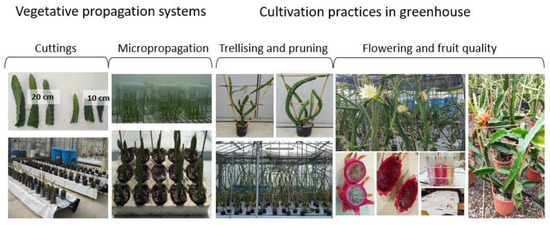
Even if pitahaya can survive with very low rainfall, many months of drought, when high-quality fruit is required, daily water supplies are needed. Regular irrigation is vital because it enables the plant to accumulate sufficient reserves not only to bloom at the most favorable moment but also to ensure the growth of the fruit. Local micro-irrigation is recommended for use. In addition to the quality of the water provided by this scheme, micro-irrigation prevents uneven and excess watering, which can result in flowers and young fruits falling off.
In Dragon Fruit Plantation, proper nutritional needs are needed to improve the yield quality of the crop. The pitahaya root system is superficial and can rapidly assimilate even the smallest quantity of nutrients.
The first year: 50 g Urea + 50 g Super phosphat/3 times/year/supporting post.
Fruit-bearing stage: 0.5 kg Urea + 0.5 kg Super phosphate + 0.5 kg potassium + 20 kg organic fertilizer/ 3 times/year/ supporting post.
Additional application of microelements such as foliar fertilizer can be used 1 time/ week when the fruits are developing.
The fertilizer must be stopped at least 10 days before the fruits be the harvest.
One of the main benefits of these crops is that it can grow in extreme temperatures and the poorest soils, but is better suited to the tropical climate with an annual rainfall of 40-60 cm that is best suited for growing. Temperatures ranging from 20°C to 30°C are considered best for the crop to grow.
Dragon Fruit can be grown on almost any soil, but sandy soils with good irrigation are generally preferred. The soil pH should be between 5.5 and 6.5 for a good crop. The beds should be at least 40-50 cm tall.
It is rich in antioxidants such as flavonoids, phenolic acid, and betacyanin. These natural substances protect the cells from destruction by free radicals—molecules that can lead to diseases such as cancer and premature aging.
It's naturally free of fat and rich in fiber. It's a good snack and it will help keep you full for longer between meals.
It can help to lower your blood sugar. Researchers believe this may be partly because it replaces dead cells in your pancreas that make insulin, a hormone that makes your body break down sugar. But studies have been done on mice, not people. It's not sure how much dragon fruit you'd have to eat to get these benefits.
It includes prebiotics, which are foods that feed healthy bacteria called intestine probiotics. Using more prebiotics in your system will increase the balance of good and poor bacteria in your intestines. In particular, dragon fruit encourages the growth of probiotics such as lactobacilli and bifidobacteria. In your stomach, these and other pathogenic compounds will destroy viruses and bacteria that cause illness.
Your immune system will be improved. Dragon fruit is high in vitamin C and other antioxidants that are good for the immune system.
It will boost the iron levels. Iron is vital for moving oxygen around your body and giving you energy, and the fruit of the dragon has iron. And the vitamin C in dragon fruit helps your body to take in and use iron.

Fruit skin colors very late in the ripening period, from green to red to rosy-pink (25 or 27 days) (depending on the species) after anthesis. It would take 30 days for H. costaricensis to be harvested. Four or five days later, the fruit reaches its maximum coloration which leads to splitting and economic loss. The first harvest begins in the 14th month (H. costaricensis) after the cuttings have been planted in the West Bengal state; the period between the flowering and the harvest is brief and varies only slightly, from (27 to 33 days) depending on the ecology. The yield depends on the density of the planting and is around (10 to 30 t/ha). The lack of a peduncle makes it difficult to choose. The current harvesting strategy of simply moving the fruit in a clockwise direction and twisting the fruit does little to no harm to the fruit. Fruits are not very fragile, but some steps should be taken to ensure a high-quality product; for example, careful handling during processing and storage, especially for H. costaricensis, whose foliated scales are brittle.
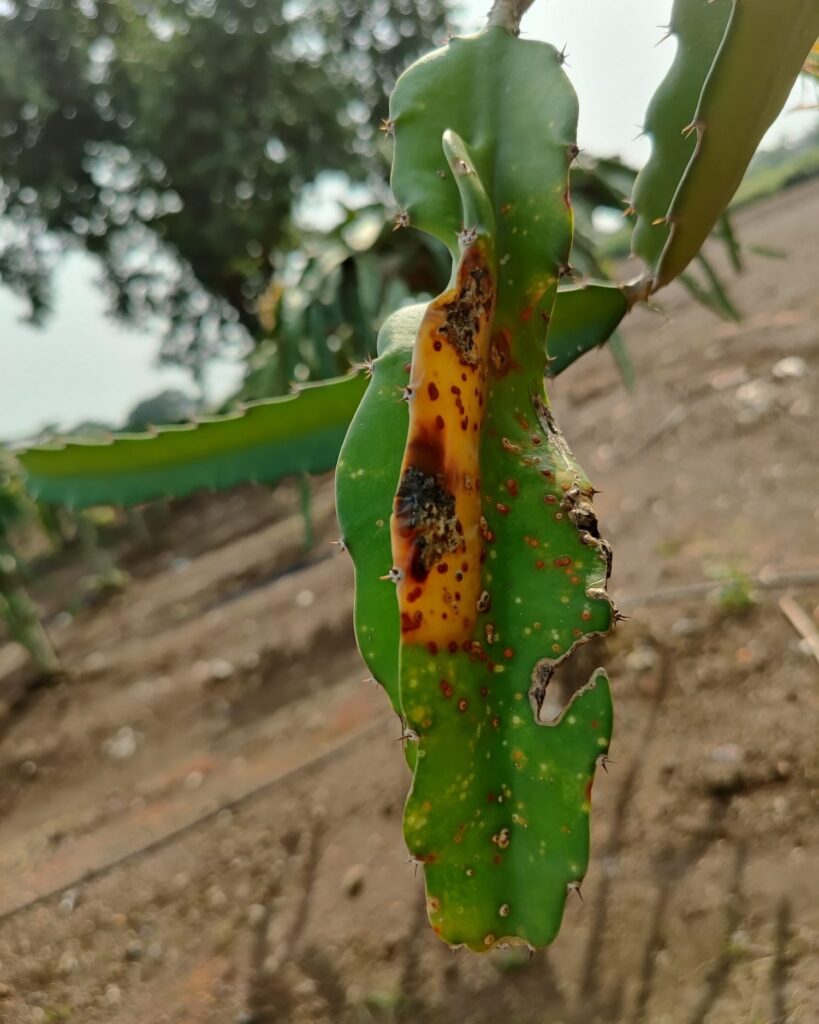

Few pests have been recorded on Hylocereus. Ants that belong to the genera Atta and Solenopsis is a very notorious pest and can cause serious damage to plants as well as flowers and fruits. Cotinus mutabilisperforates the stem and Leptoglossus zonatussucks the sap, leaving some stains and some deformation. Different varieties of aphids and scales have also been used in fruits and flowers. Rats and birds can cause serious harm, particularly to flowers and fruits, as well as too ripe fruits.
In reality, bees can be extremely successful and, after just a few hours of work, all pollen will have been harvested. The pollen must then be gathered before the bees arrive and the bees must be manually fertilized the following morning as soon as the bees have left the plantation. Different fungal (Gloeosporium agaves, Macssonina agaves, Dothiorellasp., and Botryosphaeria dothidea), viral (Cactus Virus X), and bacterial (Xanthomonassp. and Erwiniasp.) diseases are also mentioned in the literature and can have significant consequences.
Fruit formation in Dragon fruit typically starts 18-26 months after planting. Plants are usually grown in cemented poles as they need support to maintain their erect position. Poles are normally cemented to ensure durability and minimize any damage to the plant. There are about 300 poles in one acre, and one pole generally yields about 15 to 25 kg of fruit. It has been noted that a yield of 60/80 kg per pole is possible. Fruit rates are now on the market for Rs 300 to Rs 400 per kg. The general farm rate is between Rs 125 and Rs 200 per kg.
The average yield is 5–6 tons per acre, while the market price is about Rs. 200/kg. Cost to be charged every 4 months for poles, rings, cow dung, and fertilizer. There are also labor costs in addition to costs for pruning and irrigation (preferably drip irrigation) and also for netting to protect plants from birds. The recurring cost of Rs 80,000 to One Lakh per tonne has been worked out by productive growers. The fixed cost of pole, ring, and drip irrigation is to be considered and the total cost is about Rs 25.000 per tonne. Harvesting takes 18-26 months, 1.5-2 years, and between August and December. As a result, deducting all net profit costs is closer to Rs 4.50 lakes per acre for the first 2 years.

In its 2017 report, Niti Aayog called 'Doubling Farmers' Income,' said that crop diversification is a major step that all farmers must take to raise their incomes. Dragon Fruit is one of the main crops that could be adopted for this measure with an increase in supply per year. According to the Indian Council for Agriculture Research (ICAR), the fruit can be sold between Rs. 200-250 per kg and can thus make a big profit for farmers.